Calcite Components easily integrates with JavaScript frameworks and build tools, and an example repo is provided to help get started. Each example contains framework specific information. If there isn't an example using your framework or build tool of choice, then you can follow the instructions to get started using NPM.
TypeScript
When working with TypeScript, Calcite provides a full set of typings across components. To enable the typings, import the library:
import "@esri/calcite-components";Typings will provide autocomplete of component names and properties, as well as additional HTML element types:
// Created elements will implicitly have the correct type already
const loader = document.createElement("calcite-loader");
document.body.appendChild(loader);
loader.active = true;The generated types can also be explicitly typed as an element using the generated types, where the type name will be formatted with HTM:
const loader = document.querySelector(".my-loader-element") as HTMLCalciteLoaderElement;
loader.active = true;Working with Frameworks
When using TypeScript alongside Frameworks, create a TypeScript file inside your package, such as src/dependencies.ts, and add an appropriate reference directive to it:
Using React 19+:
/// <reference types="@esri/calcite-components/types/react" />Using Preact:
/// <reference types="@esri/calcite-components/types/preact" />Using Stencil:
/// <reference types="@esri/calcite-components/types/stencil" />When not using a framework, or working with an alternative framework:
/// <reference types="@esri/calcite-components" />Configuring Jest
Jest still uses CommonJS Modules (CJS) by default, and does not transform packages found in node_modules. If you didn't setup Jest to use ECMAScript Modules (ESM), you will likely see errors from Calcite when running tests, such as: SyntaxError: Unexpected token 'export'.
To resolve the module mismatch errors, Calcite components needs to be transformed from ESM to CJS using Jest's transform option:
"transformIgnorePatterns": [
"/node_modules/(?!(@esri/calcite-components*))"
]Calcite Components React
Calcite Components React is a set of React components that wrap the web components. React uses a synthetic event system, so the custom events emitted from the web components won't work with JSX in React. For example, to update a value when the calcite-slider component changes, using the standard web components, you need to save a ref to the element and add an event listener:
const sliderEl = useRef(null);
const [sliderValue, setSliderValue] = useState(50);
useEffect(() => {
sliderEl.current.addEventListener("calciteSliderUpdate", event => setSliderValue(event.target.value));
}, [sliderEl]);Using @esri/calcite-components-react, the events are connected for you:
const [sliderValue, setSliderValue] = useState(50);
<CalciteSlider onCalciteSliderUpdate={event => setSliderValue(event.target.value)} />;If you're using TypeScript, you'll also get increased type safety for your event listeners, props, etc.
Usage
To install @esri/calcite-components-react, run:
npm install @esri/calcite-components-reactThe package includes the compatible version of the web component library as a dependency, so no need to install @esri/calcite-components separately. Next, follow the instructions to get started using NPM. Lastly, import Calcite's React components you wish to use in the application:
import { CalciteButton, CalciteIcon, CalciteSlider } from "@esri/calcite-components-react";For a complete setup, check out the React example.
Gotchas
Boolean attributes
Passing boolean attributes to Calcite's React components converts the value to a string, which is due to React compatibility issues with web components. There are Stencil and React issues for the problem. As a result, it is not recommended to set disabled={false}. The workarounds for boolean attribute values are:
- Don't set the attribute
- Use
undefinedinstead offalse
For example, this Calcite will be selected:
const selected = false;
<CalciteListItem key={0} label="Fried Egg Jellyfish" value="jellyfish" selected={selected}></CalciteListItem>;However, none of these items will be selected:
const selected = false;
<CalciteListItem key={1} label="Satanic Leaf-Tailed Gecko" value="gecko"></CalciteListItem>
<CalciteListItem key={2} label="Red-Lipped Batfish" value="batfish" selected={undefined}></CalciteListItem>
<CalciteListItem key={3} label="Star-Nosed Mole" value="mole" selected={selected ? true : undefined}></CalciteListItem>Visual Studio IntelliSense
Calcite supports IntelliSense in Visual Studio Code. You can quickly add components and their attributes or properties in the Visual Studio Code editor, where accompanying documentation will help you along the way.
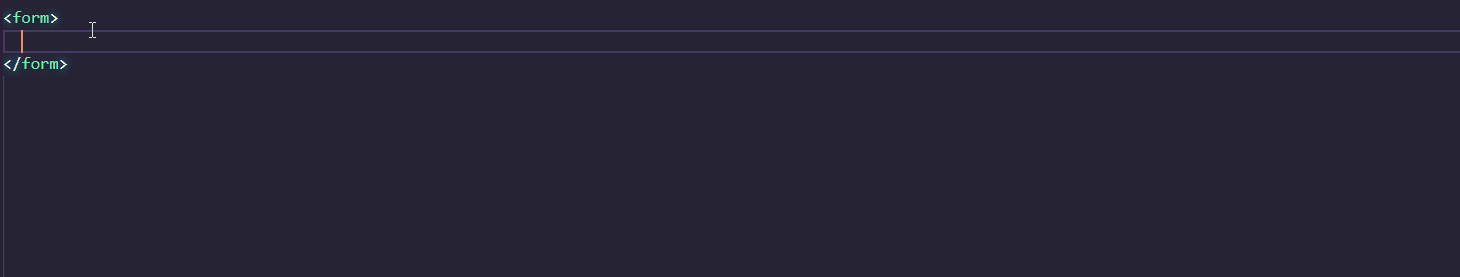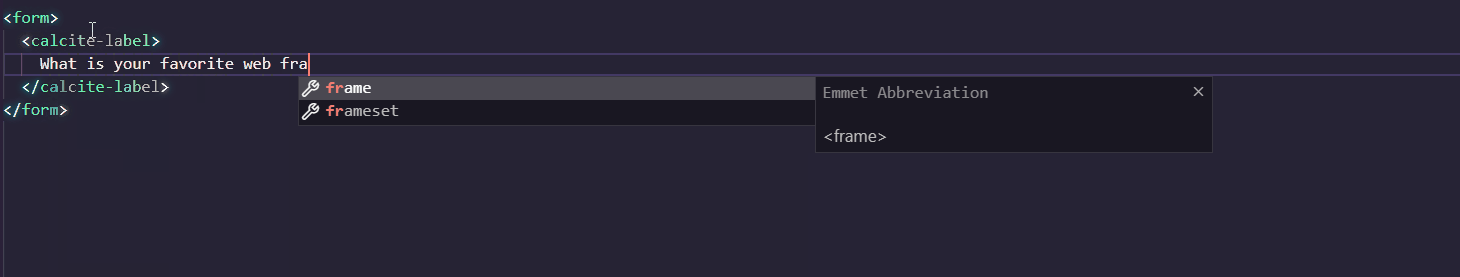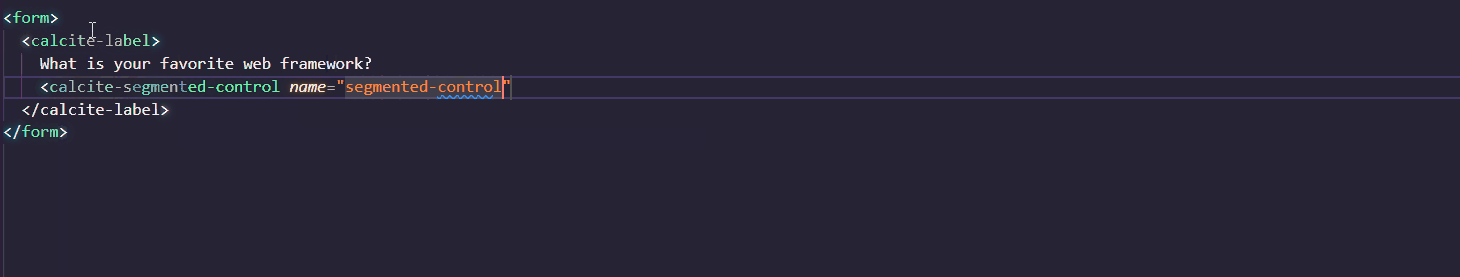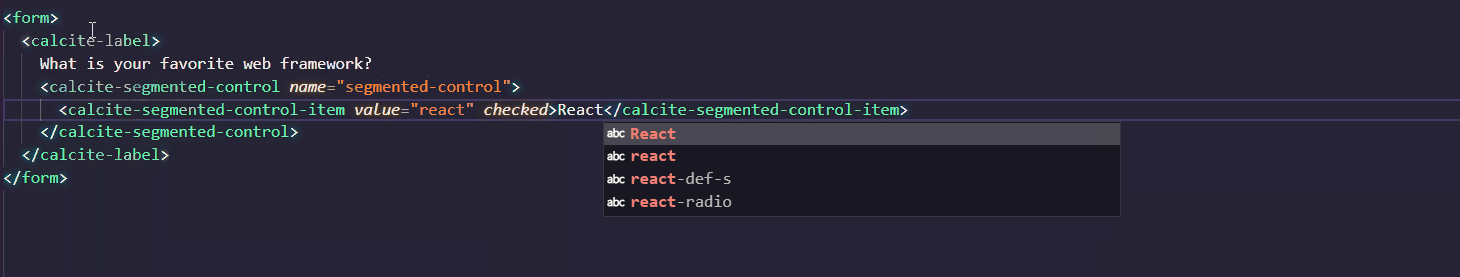
To setup IntelliSense, add the following to the .vscode/settings.json file in your project:
"html.customData": [
"./node_modules/@esri/calcite-components/dist/docs/vscode.html-custom-data.json"
],
"css.customData": [
"./node_modules/@esri/calcite-components/dist/docs/vscode.css-custom-data.json"
]For more detailed information on IntelliSense, visit the Visual Studio Code IntelliSense documentation.